Help formatting and theming¶
Formatting settings¶
In Cloup we can distinguish two groups of formatting settings:
parameters of commands/mixins classes
align_option_groups– see here;align_sections– similar toalign_option_groupsbut for subcommand sections;show_constraints– whether to include the “Constraints” section (see here);
since v0.8, these parameters are also available as
Contextparameters.parameters of the
HelpFormatter, includingtheme(click onHelpFormatterto see the full list); these parameters can be passed to bothContextand commands using the parameterformatter_settings, which is a dictionary.
In both cases, commands settings override context settings.
In the case of formatter_settings, the final settings used by a command are
obtained by merging the dictionaries like following:
{**ctx.formatter_settings, **command.formatter_settings}.
Context settings propagate to subcommands, while command settings don’t.
An example¶
Tip
In Cloup, you can use the static methods Context.settings() and
HelpFormatter.settings() to create dictionaries without leaving your
IDE (to check the docs).
from cloup import Context, command, group, HelpFormatter, HelpTheme
CONTEXT_SETTINGS = Context.settings(
align_option_groups=False,
align_sections=True,
show_constraints=True,
formatter_settings=HelpFormatter.settings(
max_width=100,
max_col1_width=25,
min_col2_width=30,
indent_increment=3,
col_spacing=3,
row_sep='\n',
theme=HelpTheme.light()
)
)
@group(context_settings=CONTEXT_SETTINGS)
# ...
def main(...):
...
# This command overrides some of CONTEXT_SETTINGS values
@main.command(
align_option_groups=True,
formatter_settings=HelpFormatter.settings(
max_col1_width=30,
)
)
# ...
def cmd(...):
...
Theming¶
A HelpTheme is a collection of styles for several elements of the help page.
A “style” is just a function (or a callable) that takes a string and returns a
styled version of it. This means you can use your favorite styling/color library
(like rich, colorful etc) with it.
Given that Click has some built-in basic styling functionality provided by the
function click.style(), Cloup provides the Style class, which
wraps click.style to facilitate its use with HelpTheme.
Tip
Cloup also provides an enum-like class Color containing all
colors supported by Click.
The following picture links HelpTheme arguments to the corresponding visual
elements of the help page (only epilog is missing):
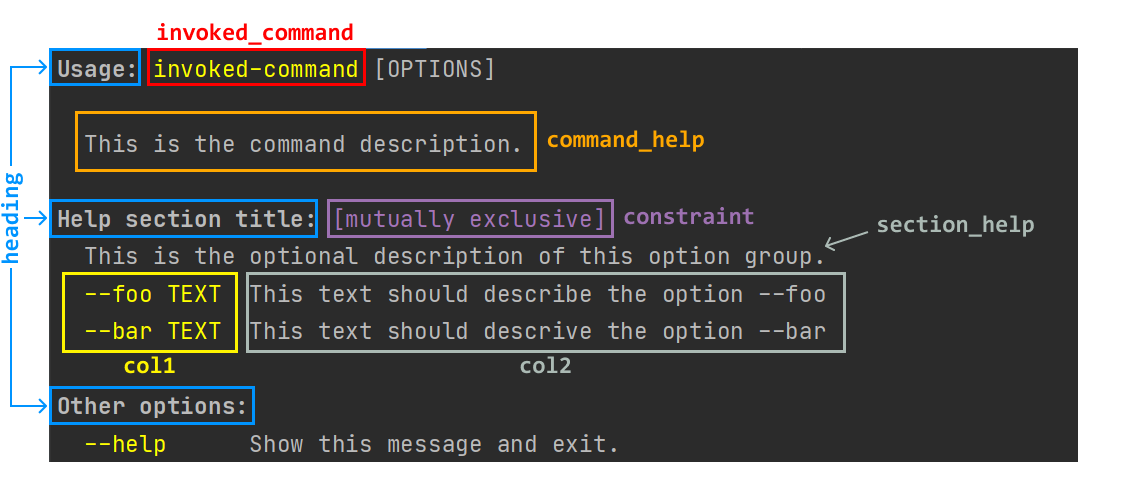
The above image was obtained with the following theme:
HelpTheme(
invoked_command=Style(fg='bright_yellow'),
heading=Style(fg='bright_white', bold=True),
constraint=Style(fg='magenta'),
col1=Style(fg='bright_yellow'),
)
For an always up-to-date list of all possible arguments these classes take, refer to the API reference:
|
A collection of styles for several elements of the help page. |
|
Wraps |
How to set a theme¶
You must provide a theme as part of the formatter_settings dictionary,
as shown in the example above.
Available themes (and how to override parts of them)¶
Cloup provides two reasonable themes:
A theme assuming a dark terminal background color. |
|
A theme assuming a light terminal background color. |
You probably want to select a theme based on the terminal background color in use. Nonetheless, Cloup doesn’t currently provide a way to get it (any suggestions are welcome).
If you want, you can use the default themes as a base and change only some of
the styles using HelpTheme.with_(), e.g.:
theme = HelpTheme.dark().with_(
col1=Style(fg=Color.bright_green),
epilog=Style(fg=Color.bright_white, italic=True)
)
The linear layout for definition lists¶
When the terminal width is “too small” for a standard 2-column definition lists,
Cloup HelpFormatter switches to a “linear layout”, where
the option description is always printed below the option name, with an indentation increment of at least 3 spaces
all definitions are separated by an empty line.
The following tabs compare the --help of the manim example (“aligned” and
“non-aligned” refer to the align_option_groups argument):
Usage: manim render [OPTIONS]
SCRIPT_PATH
[SCENE_NAMES]...
Render some or all scenes defined in a Python
script.
Global options:
-c, --config_file TEXT
Specify the configuration file to use for
render settings.
--custom_folders
Use the folders defined in the
[custom_folders] section of the config
file to define the output folder
structure.
--disable_caching
Disable the use of the cache (still
generates cache files).
--flush_cache
Remove cached partial movie files.
--tex_template TEXT
Specify a custom TeX template file.
-v, --verbosity [DEBUG|INFO|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL]
Verbosity of CLI output. Changes ffmpeg
log level unless 5+.
[...]
Usage: manim render [OPTIONS]
SCRIPT_PATH
[SCENE_NAMES]...
Render some or all scenes defined in a Python
script.
Global options:
-c, --config_file TEXT Specify the
configuration
file to use for
render settings.
--custom_folders Use the folders
defined in the
[custom_folders]
section of the
config file to
define the output
folder structure.
--disable_caching Disable the use
of the cache
(still generates
cache files).
--flush_cache Remove cached
partial movie
files.
--tex_template TEXT Specify a custom
TeX template
file.
-v, --verbosity [DEBUG|INFO|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL]
Verbosity of CLI
output. Changes
ffmpeg log level
unless 5+.
[...]
Usage: manim render [OPTIONS]
SCRIPT_PATH
[SCENE_NAMES]...
Render some or all scenes defined in a Python
script.
Global options:
-c, --config_file TEXT Specify the
configuration file to
use for render
settings.
--custom_folders Use the folders
defined in the
[custom_folders]
section of the config
file to define the
output folder
structure.
--disable_caching Disable the use of
the cache (still
generates cache
files).
--flush_cache Remove cached partial
movie files.
--tex_template TEXT Specify a custom TeX
template file.
-v, --verbosity [DEBUG|INFO|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL]
Verbosity of CLI
output. Changes
ffmpeg log level
unless 5+.
--notify_outdated_version / --silent
Display warnings for
outdated
installation.
[...]
The linear layout is controlled by the min_col2_width argument of HelpFormatter.
The linear layout is used when the available width for the 2nd column is below
min_col2_width, which defaults to 35.
You can disable the linear layout settings min_col2_width=0.
You make the linear layout your default layout by settings min_col2_width to
a large number, possibly math.inf.
Minor differences with Click¶
The width of the 1st column of a definition list is computed excluding the rows that exceeds
col1_max_width; this results in a better use of space in many cases, especially withalign_option_groups=False.The default
short_help’s of commands actually use all the available terminal width (in Click, they don’t; see “Related issue” of this Click issue)The command epilog is not indented (this is just my subjective preference).